Dreamcast Image Builder/Creating Mods: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
You can create new mods by clicking the <code>+</code> button to the bottom right of the mod list. User created mods are placed in the <code>mods</code> folder in the same location as <code>DreamcastImageBuilder.exe</code>. Each mod is placed in a subfolder within the <code>mods</code> folder. | You can create new mods by clicking the <code>+</code> button to the bottom right of the mod list. User created mods are placed in the <code>mods</code> folder in the same location as <code>DreamcastImageBuilder.exe</code>. Each mod is placed in a subfolder within the <code>mods</code> folder. | ||
When you create a new mod, you can import a DCP file created by Universal Dreamcast Patcher by clicking the <code>Import...</code> button. The contents of the DCP file will be added to the mod structure. | When you create a new mod, you can import a DCP file created by [https://github.com/DerekPascarella/UniversalDreamcastPatcher Universal Dreamcast Patcher] by clicking the <code>Import...</code> button. The contents of the DCP file will be added to the mod structure. | ||
The sections below describe the information contained in mods. Some of this data is filled in automatically when you create mods using the <code>+</code> button in the UI. | The sections below describe the information contained in mods. Some of this data is filled in automatically when you create mods using the <code>+</code> button in the UI. | ||
Revision as of 00:13, 14 October 2025
Dreamcast Image Builder comes with several built-in mods, and it also supports custom made mods.
You can create new mods by clicking the + button to the bottom right of the mod list. User created mods are placed in the mods folder in the same location as DreamcastImageBuilder.exe. Each mod is placed in a subfolder within the mods folder.
When you create a new mod, you can import a DCP file created by Universal Dreamcast Patcher by clicking the Import... button. The contents of the DCP file will be added to the mod structure.
The sections below describe the information contained in mods. Some of this data is filled in automatically when you create mods using the + button in the UI.
Creating mod.ini
The main information is stored in the mod.ini file. It has the following sections. Quotation marks are not used.
Main Mod Information
Here is an example mod.ini:
Name=Mod name (used in the UI and for mod sorting/selection) Author=Mod developer Version=Mod version GameVersions=Comma-separated list of game IDs compatible with this mod Discs=1,2 Description=Mod description (used in the UI; you can use \n for line breaks DeleteFiles=delete.bin,folder\delete2.bin
Use the Discs field to specify a comma-separated list of compatible discs in mods for multi-disc games (no spaces before or after the commas). For example, if your mod is meant to work with Shenmue Disc 3 (but not discs 1 or 2), write Discs=3. If the Discs field is not specified, the mod will be compatible with any disc ID.
The DeleteFiles field is used to specify which files to exclude from the modified image. For example, if you want to delete the file in GD Root\SONICADV\ADV00.PRS, write DeleteFies=SONICADV\ADV00.PRS. You can delete multiple files and folders by using a comma-separated list (no spaces before or after the commas).
The GameVersions field is required for game compatibility check. Usually it's a single game ID. A mod compatible with multiple versions of the game can be set up like this:
Name=Debug Mode Author=woofmute Version=1.0 Description=Enables the Debug menu GameVersions=MK-5119250V1.00320011004,HDR-0178 V1.00320011004
In the above example, MK-5119250V1.00320011004 is the European version of Rez, and HDR-0178 V1.00320011004 is the Japanese version.
Patch Data
The mod.ini file can also contain patches for specific files. Each file can have multiple patches. The patches are stored in the following format:
[Filename] ; Patch Description (optional) Address,Type,Count=Value ; Patch 2 Description (optional) Address,Type,Count=Value
Filename is the name of the file to patch, such as 1ST_READ.BIN.
- Note that the filename must be in square brackets (so that it becomes a section in the INI file). The section indicates the beginning of the patch list for the specified filename.
- If the file is not at the root of the GD drive, use relative paths to specify its location. For example, if the file
STG01.PRSis located in theSONICADVfolder, the filename will beSONICADV\STG01.PRS. - If the filename has the PRS extension, it will be extracted, patches will be applied to decompressed data and the edited file will be repacked back to PRS.
Patch Description is for better readability. It will be output to the log when the patch is applied.
- Patch description must begin with
;. - Patch description must be inside the INI section (the line after the filename in square brackets) and before the patch line.
- If there are multiple patch descriptions, only the first will be displayed for the whole patch.
Address is the offset in the file where the patch will be written. It's a hexadecimal value in Big Endian format, such as 168E6C for offset 0x168E6C.
- If
Addressis preceded by;, the patch will not be applied.
Type specifies the kind of value to be written. The following patch types can be used. Patch type names are case insensitive.
HexBytes or hb: a sequence of bytes in hexadecimal format in the order that they will be written.
HexBytesBigEndian, hexbytesbe, hbbe or be: a sequence of bytes in hexadecimal format written in the reversed order.
Sint8, si8 or s8: Signed 8-bit integer (decimal).
Uint8, ui8 or u8: Unsigned 8-bit integer (decimal).
Sint16, si16 or s16: Signed 16-bit integer (decimal).
Uint16, ui16 or u16: Unsigned 16-bit integer (decimal).
Sint32, si32 or s32: Signed 32-bit integer (decimal).
Uint32, ui32 or u32: Unsigned 32-bit integer (decimal).
Float32, float or f32: A 32-bit floating point value.
String or str: An ASCII string.
StringNullTerminated or stringnull or strnull: A null-terminated ASCII string.
File: A sequence of bytes read from an external file.
FileI: A sequence of bytes read from an external file (insert bytes instead of overwriting).
Pointer or p: Scans the file for pointers to the address specified in Address and replaces them with pointers to the address specified in Value.
- The default
TypeisHexBytes. If you only need to write a sequence of bytes once, you don't need to specify the patchTypeandCount. However, you do need to specifyTypeif you are writing data more than once.
Count is the number of times to repeat the writing operation. For example, specifying Count of 3 for a HexBytes value FF will make the program write FF FF FF, and specifying Count of 2 for a String value of TEXT will make the program write TEXTTEXT (54 45 58 54 54 45 58 54).
- For the
StringNullTerminatedpatch, repeated writing will also write the null terminator. For example, writing a null-terminatedTEXTstring twice will result in the following bytes:54 45 58 54 00 54 45 58 54 00 - If
Countis0, the patch will not be applied. - For the
Pointerpatch,Countis not applicable and will be ignored if specified. - The default value for
Countis1. If you need to write data only once, you do not have to specify it.
Value is the value or the sequence of bytes to be written.
- For
HexBytesandHexBytesBigEndianpatches,Valuecan be any number of hexadecimal values represented in ASCII. For example,A1 B2 C3 D4will write bytes0xA1,0xB2,0xC3and0xD4. The same value for the Big Endian variation of the patch will write0xD4,0xC3,0xB2and0xA1. - For integer patches,
Valueis an integer in the decimal format, such as-100or255. - For the
Floatpatch,Valueis a floating point number such as3.45. - For the
StringandStringNullTerminatedpatches,Valueis an ASCII string, such asSEGA(without quotes). - For the
Filepatch,Valueis the location of the data file, such ashack\data.bin. The file will be loaded from the mod folder. Relative paths can be used. - For the
Pointerpatch,Valueis the replacement pointer value in the Big Endian format, such as8C5C1CD2(for0x8C5C1CD2).
Examples
[SONICADV\SHOOTING.PRS] ; Write an unsigned 1-byte integer value of 128 (0x80) once at address 0x5556C. 5556C,u8,1=100
Result: SONICADV\SHOOTING.PRS: 0x5556C -> 80.
[1ST_READ.BIN] ; Write a signed 1-byte integer value of -1 (0xFF) twice at address 0x5556D. 5556D,s8,2=-1
Result: 1ST_READ.BIN: 0x5556D -> FF FF.
[1ST_READ.BIN] ; Write a float value of 1556.0 (0x44C28000) once at address 0xC53F0. C53F0,float,1=1556.0
Result: 1ST_READ.BIN: 0xC53F0 -> 00 80 2C 44
[1ST_READ.BIN] ; Write the data from `mod folder\sheep\model.bin` once to offset 0x166284 166284,file,1=sheep\model.bin
Result: 1ST_READ.BIN: 0x166284 -> (contents of model.bin)
[1ST_READ.BIN] ; Write the null-terminated "SEGA" ASCII string twice at 0x1000. 1000,stringnull,2=SEGA
Result: 1ST_READ.BIN: 0x1000 -> 53 45 47 41 00 53 45 47 41 00
Additional Examples and Tips
HexBytesis the default patch format, and you can omitTypeandCountif you only need to write a sequence of bytes once. Example:
[SONICADV\MOVIE.BIN] ; Write 09 00 to 0x2A4 and 0x28D 02A4=09 00 028D=09 00
Result: SONICADV\MOVIE.BIN: 02A4 -> 09 00; 028D -> 09 00
- The default value for
Countis 1. If you don't need to write data more than once, you can omitCount:
[1ST_READ.BIN] ; Write the "SEGA" ASCII string at 0x1000. 1000,string=SEGA
Result: 1ST_READ.BIN: 0x1000 -> 53 45 47 41
[1ST_READ.BIN]
- Write the value 0x8C0112B4 to offset 0x168E6C
Result: 1ST_READ.BIN: 168E6C -> B4 12 01 8C
- You can combine multiple patch types in a single line. The data will be written once in a sequential order. The
Pointerpatch type is not supported in this mode.
[1ST_READ.BIN] ; Chao Race start position for Sonic (replaces MR Garden) 15F4CC,Uint16/Uint16/float/float/float/Uint16=40/0/-170/60/-25/32517
Result:
1ST_READ.BIN: 15F4CC -> 28 00 15F4CE -> 00 00 15F4D0 -> 00 00 2A C3 15F4D4 -> 00 00 70 42 15F4D8 -> 00 00 C8 C1 15F4DC -> 05 7F
File Replacement
Mods can replace files in two ways:
- Files in the
includefolder (+ files in its subfolders) are copied to GD root without preserving folder hierarchy. - Files and folders in the
gdrootfolder are copied with folder hierarchy.
Examples:
If your mod has a file include\textures\text1.pvr, it will be copied to GD Root\text1.pvr.
If your mod has a file gdroot\textures\text2.pvr, it will be copied to GD Root\textures\text2.pvr.
In addition, the following changes are supported:
- You can replace
IP.BINby putting your own version of it in the mod's folder, although it is not recommended. Note that even if you add your ownIP.BIN, the program may apply additional changes to it such as binhack, region patch etc. - Files with the
.xdeltaextension will be applied as xdelta patches (see below).
Example: If your mod has a file gdroot\1ST_READ.BIN.xdelta, it will be applied as a diff file to GD Root\1ST_READ.BIN.
NOTE! The program makes a list of xdelta patches in all mods and applies them to original files first, before mods are applied. You cannot apply more than one xdelta patch to a single file.
Additional Fields in mod.ini
RequiredCodes
The RequiredCodes field specifies a comma-separated list of cheat codes that are required for the mod to function. These codes will be auto-enabled during build process if this mod is enabled.
Example:
Name=Widescreen test RequiredCodes=Widescreen culling fix
ReplacePointers
The ReplacePointers field in the main section lists files where pointer replacements will be made. Example:
Name=Pattern Test Description=Test pattern replacement ReplacePointers=AL_GARDEN01.PRS
For each file listed in ReplacePointers, a pointer replacement list will be loaded from an INI file based on the original filename with the .INI extension (AL_GARDEN01.PRS.INI for the example above). If it is missing, the file pattern.ini will be loaded instead. This can be useful for patching the same pointers across multiple files.
- If the file's extension is PRS, the program will decompress it, apply pointer replacements to decompressed data and recompress it back to PRS.
Pointer replacement lists are text files in the following format. Each line specifies a pointer replacement.
Pointer name,Original address,Replacement address
Pointer name is meant to provide the patch's description for better readability.
- If the pointer name starts with
;, the patch will not be applied.
Original address is the pointer value that will be replaced.
Replacement address is the value that will be written as a replacement.
Example:
njpushmatrix,8C5A65B8,8C5BED18 njtranslatev,8C5A7140,8C5BF8A0 ;DrawObject,8C030592,8C5FDEB2
The njpushmatrix replacement will search for pointers to 0x8C5A65B8 and replace them with pointers to 0x8C5BED18.
The njtranslatev replacement will search for pointers to 0x8C5A7140 and replace them with pointers to 0x8C5BF8A0.
The DrawObject pointer replacement will not be applied.
Adding Submods
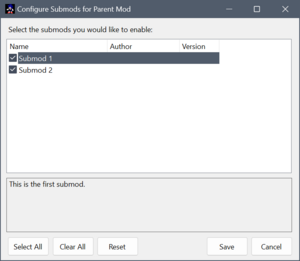
Each mod can have one or more "submods". A submod has the same capabilities as a regular mod, but it doesn't appear on the main list of mods. Submods are only applied when the parent mod is enabled, and the submod is also enabled in the parent mod's configuration.
To add submods, use the Submods field in the main section of the mod.ini file.
Submods is a comma-separated list of relative paths to submods' INI files. Submods must be placed in separate subfolders within the parent mod's folder. Submod INI files can have any name except mod.ini.
DefaultSubmods is a comma-separated list of submod names (matching the Name field in the submod's INI file) that are active by default. If this key is missing in the INI file, all submods will be enabled by default.
mod.ini
Name=Test Parent Mod Description=This mod demonstrates usage of submods. GameVersions=610-7029 V1.00019981016 Submods=submod1\submod1.ini,submod2\submod2.ini DefaultSubmods=Submod 1, Submod 2
In the case of the example above, the file structure of the mod should be as follows.
The submod1 folder contains submod1.ini and the submod2 folder contains submod2.ini.
submod1\submod1.ini
Name=Submod 1 Description=This is the first submod. GameVersions=610-7029 V1.00019981016
submod2\submod2.ini
Name=Submod 2 Description=This is the second submod. GameVersions=610-7029 V1.00019981016
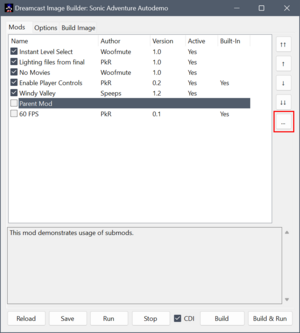
The player can enable or disable submods using the ... button that appears to the right of the mod list when a mod with submods is highlighted.
 |
 |
|---|